ARFI
What is Liver Elastography (ARFI)?
Liver Elastography is a new technology that measures stiffness of the Liver tissues. It is also known as Tissue Strain Analysis or Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging etc. These two applications are available only in ACUSON S 2000 system from Siemens.
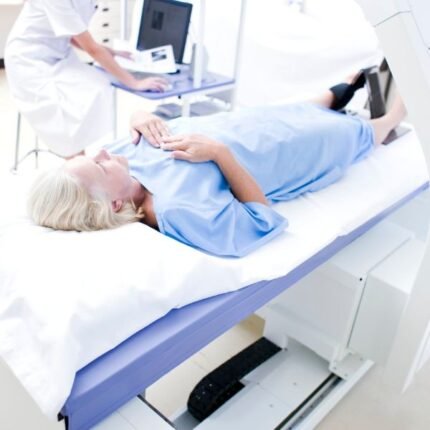
BMD (Dexa Scan)
How the Test is Performed
A bone mineral density (BMD) examination quantifies the presence of calcium and various mineral types within a specific bone region. This assessment aids your healthcare professional in identifying osteoporosis and assessing the likelihood of bone fractures.
Bone density testing can be done several different ways.
The most common and accurate way uses a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. DEXA uses low-dose x-rays. (You receive more radiation with a chest x-ray.)